TSC INTERVIEWQUESTIONS & NOTES
- MINISTRY OF EDUCATION
- What is the structure of the ministry of education?
- Cabinet secretary
- Principal secretaries: state dep’t of science & technology, state dep’t of education
- Science & technology secretary/education secretary- Professional Arm (SAGAS & Administration Department)
- Directors of education- science & tech, technical & vocational edn, primary edn, sec & tertiary edn, university edn, schools audit,adult & continuing edn, youth training.
- Administration support
- County director of education, science and technology
- What is the overall role of the cabinet secretary in charge of education?
- Provide free and compulsory basic education to every child
- Ensure compulsory admission and attendance of children of compulsory school age at school or an institution of offering basic education.
- Ensure that children belonging to marginalised, vulnerable, or disadvantaged groups are not discriminated against and prevented from pursuing and completing basic education
- Provide human resource including teaching and non-teaching staff, infrastructure including school buildings; learning and teaching equipment’s; and appropriate financial resources
- Ensure quality basic education conforming to the set standards and norms;
- Provide special education and training facilities for talented and gifted pupils and pupils with disabilities
- Ensure compulsory admission, attendance, and completion of basic education by every pupil;
- Monitor functioning of schools.
- What is the role of the principal secretary and education secretary?
Principal secretary
- Is the top civil servant and the accounting officer in the ministry
- Executes policy matters concerning education
- Formulates and implement’s policies
- In charge of overall supervision and control matters related to parastatal bodies and institutions under the ministry of education e.g. JKF, KICD etc.
- Chairs the cabinet management committee and he is also a member of board of higher institutions of learning and education councils e.g. UON council
Continue Reading:
- Best TSC Interview Questions and Answers {TSC Official}
- TSC interview questions and their answers- 2024 recruitment
- Latest TSC Interview Questions, Answers and Guiding Notes
- TSC Interview Questions, Notes and Guidelines
- Latest TSC list of Most Common Promotion Interview Questions and Answers (Score above 80%)
- TSC Interview Questions So as to get promotion to next grade
- TSC Interview Questions, Answers & Notes
- Latest TSC Promotions Interview Questions and Answers 2024
- TSC promotion interviews questions and answers; Prepare well
- TSC latest promotion interviews marking scheme and Questions
- Latest TSC Interview areas, questions and new marking scheme/ Score sheet for teachers seeking TSC Promotions; This is all you need to know
- TSC teachers interview promotion questions and their answers- 2024
- Questions asked in TSC promotion interviews & answers
- TSC Promotion Interview in 3 Phases: Interview dates, Venues and Questions
- Latest TSC Promotion Interview Questions, Marking Scheme, Scoring Areas
- TSC promotion interview questions and their answers
- TSC Promotion Interview Areas, Questions And Answers plus Marking Scheme
- TSC promotions interview questions, scoring guide and marks per job group
- TSC promotions interview areas, questions and how to answer
- Latest TSC Promotion interview questions and answers
- Expected TSC promotions interview questions and answers 2024
- New Latest TSC Grading System, TSC Job Groups and Their Salary Scale
- TSC frequently asked questions and answers: TSC News
- Teachers Service Commission, TSC, Kenya – Latest News, Website, Contacts, Portals Complete guide
Education secretary
- Who publishes for the ministry of education?
- What is the role of KICD, inspectorate and KNEC?
KICD
- Advise the government on matters pertaining to curriculum development
- Evaluate, vet, and approve for application in Kenya, any local or foreign curricula and curriculum support materials in relation to the levels of education and training.
- implement the policies relating to curriculum development in basic and tertiary education and training.
- Develop, review and approve programmes, curricular and curriculum support materials that meet international standards for – (i) early childhood care, development, and education; (ii) pre-primary education, (iii) primary education, (iv) secondary education, (v) adult, continuing and non-formal education, (vi) teacher education and training, (vii) special needs education, and (viii) technical and vocational education and training.
- Initiate and conduct research to inform curriculum policies, review and development.
- Collect document and catalogue information on curricula, curriculum support materials and innovations to create a data bank and disseminate the information to educational institutions, learners, and other relevant organisations.
- Print, publish and disseminate information relating to curricula for basic and tertiary education and training.
- Collaborate with other individuals and institutions in organizing and conducting professional development programmes for teachers, teacher trainers, quality assurance and standard officers and other officers involved in education and training on curriculum programmes and materials
- Develop, disseminate and transmit programmes and curriculum support materials through mass media, electronic learning, distance learning and other mode of delivering education and training programme materials.
- Promote appropriate utilisation of technology to enhance3 innovations and achievements of a knowledge based economy.
- Offering consultancy services in basic and tertiary education and training.
- Incorporate national values, talent development and leadership values in curriculum development.
- Receive, consider, develop and review curriculum proposals.
DIRECTORATE OF QUALITY ASSURANCE AND STANDARDS
- Establishing, maintaining, and improving standards in all basic and training institutions
- Quality assurance and standards assessment of basic educational and training
- Coordination, organization, and implementation of co-curriculum activities at national and international levels
- Vetting of expatriate teachers and institutions offering international curriculum
- Liaison with KNEC on assessment of pre-service primary, ECDE and diploma teacher education examination teaching practice
- Policy formulation and implementation on matters related to quality assurance
- Developing of assessment standards
- Liaison with KNEC in moderation, awards and National assessment and learning achievement (NASMLA) and examinations
- Liaison with KICD on curriculum design, development and evaluation.
- Talent identification and development in schools and colleges
- Advising the cabinet secretary and principal secretary on all matters of quality assurance and standards in the country.
KNEC
- It performs the administration of primary, secondary, and tertiary examinations on behalf of the Government.
- It test-runs draft curricula and carries out equivalence procedures of certificates and diplomas issued by other examining bodies.
- It awards certificates and diplomas to successful candidates in such examinations
- It makes rules regulating the conduct of examinations and for all purpose incidental where to
- Differentiate between the roles of the BOM and PTA in a School.
BOM
(a)promote the best interests of the institution and ensure its development;
(b) promote quality education for all pupils in accordance with the standards set under this Act or any other written law;
- c) ensure and assure the provision of proper and adequate physical facilities for the institution;
(d) manage the institution’s affairs in accordance with the rules and regulations governing the occupational safety and health;
(e) advise the County Education Board on the staffing needs of the institution;
(f) determine cases of pupils’ discipline and make reports to the County Education Board;
(g) prepare a comprehensive termly report on all areas of its mandate and submit the report to the County Education Board;
(h) facilitate and ensure the provision of guidance and counseling to all learners;
(i) provide for the welfare and observe the human rights and ensure safety of the pupils, teachers, and non-teaching staff at the institution;
(j) encourage a culture of dialogue and participatory democratic governance at the institution;
(k) promote the spirit of cohesion, integration, peace, tolerance, inclusion, elimination of hate speech, and elimination of tribalism at the institution;
(l) encourage the learners, teachers and non-teaching staff and other, parents and the community, and other stakeholders to render voluntary services to the institution;
(m) allow reasonable use of the facilities of the institution for community, social and other lawful purposes, subject to such reasonable and equitable conditions as it may determine including the charging of a fee;
(n) administer and manage the resources of the institution;
(o) receive, collect and account for any funds accruing to the institution;
(p) recruit, employ and remunerate such number of non-teaching staff as may be required by the institution in accordance with this Act; and
- q) perform any other function to facilitate the implementation of its functions under this Act or any other written law.
PTA
The functions of the Parents Association shall be to—
(a) promote quality care, nutritional and health status of the pupils;
(b) maintain good working relationship between teachers and parents;
(c) discuss, explore, and advise the parents on ways to raise funds for the physical development and maintenance;
(d) explore ways to motivate the teachers and pupils to improve their performance in academic and co- curricular activities;
(e) discuss and recommend charges to be levied on pupils or parents;
(f) undertake and oversee development projects on behalf of the whole Parents Association.
(g) assist the school management in the monitoring, guidance, counseling and disciplining of pupils; and
(h) discuss and recommend measures for the welfare of staff and pupils.
- What is the composition of the board of management of a school and how are they chosen?
The Board of Management established under section 55 shall consist of the following members appointed by the County Education Board:
(a) six persons elected to represent parents of the pupils in the school or local community in the case of county secondary schools;
(b) one person nominated by the County Education Board;
(c) one representative of the teaching staff in the school elected by the teachers;
(d) three representatives of the sponsors of the school;
(e) one person to represent special interest groups in the community; and
(f) one person to represent persons with special needs;
(g) a representative of the students’ council who shall be an ex officio member
- What does the ‘orange Book’ contain?
Approved list of text books and other instructional materials for schools.
- THE TEACHERS SERVICE COMMISSION
- What is the structure of TSC?
- The commissioners- chairperson, vice chairperson, commissioners (7)
- The secretary & deputy commission secretary
- Directors- HRM, Administration, Teacher management, Finance, ICT, Accounts & Internal audit
- Senior deputy directors
- Deputy directors
- Assistant deputy directors
- Principal officers
- Chief/senior officers
COUNTY STRUCTURE
- TSC county director
- TSC deputy county director (2)
- Assistant deputy directors-ICT, Teacher management, HRM, Procurement and stores, Accounts,
- County principal officers- ICT, Data analyst, Quality & standards, Staffing, Disciple, HRM, Pension, procurement, Stores, Accountant, Corporate communication, integrity assurance, services, AIDs control unit, Internal auditor,
- County chief officers-
- What are the functions of TSC?
- Registration of trained teachers
- Recruitment and employment of registered teachers
- Assign teachers employed by the commission for service in any public school or institution;
- Manage the payroll for teachers in employment
- Promotion and transfer of teachers
- Exercise disciplinary control over teachers
- Formulate policy to achieve its mandate
- Ensure teachers comply with the teaching standards prescribed under the commission Act
- Review the demand and supply of teachers
- Review the standards of education and training of persons entering the teaching service
- Facilitate career progression and professional development for teachers in the teaching service including the appointment of head teachers and principals
- Monitor the conduct and performance of teachers in the teaching service.
- What empowers TSC to carry out their functions?
The constitution of Kenya Article 237(1)and the teachers service commission Act
- What is the role of secretary of TSC?
- The head of the secretariat
- The accounting officer of the commission
- The custodian of records of the commission
- Execute the decisions of the commission
- Assign duties to and supervise the staff of the commission
- Facilitate, coordinate, and ensure the execution of the commission mandate
- Ensure staff compliance with public ethics and values
- Performs general administration of the commission
- Perform any other duties as may be assigned by the commission
- Name three types of retirement benefits.
Pension, marriage & death Gratuity, and work injury benefits
- When is a teacher given, study leave with pay?
- When selected for training by the commission, MOE or ministry of state for public service
- UT teachers in employment of TSC studying for a PGDE in approved universities
- UT technical teachers undertaking professional training in KTTC.
- Trained technical teachers & lecturers studying higher diploma or master’s degree in engineering, applied science, business studies and technical education
- P1/AT IV admitted in KISE to study a diploma in special education
- Teachers admitted in accredited local universities for master’s degrees in selected areas.
- Under what circumstances can a teacher request for a special leave?
When a teacher has been selected, and appointed to attend a meeting, workshop, study tour or seminar for a duration not exceeding three months, which is of national interest or is relevant to education and teaching service
- Who is the TSC agent in your school
The head of the institution
- KICD
- Define curriculum, what is co-curricular?
CURRICULUM
“curriculum” means all the approved subjects taught or programmes offered and includes all the activities provided at any institution of basic education;
CO-CURRICULAR
Are activities, programmes, and learning experiences which complement what students learn in the academic curriculum in school.
- Distinguish between formal and non-formal curriculum?
Formaleducation” means the regular education provided in the system of schools, and other formal educational institutions;
Non-formaleducation” means any organized educational activity taking place outside the framework of the formal education system and targets specific groups/categories of persons with life skills, values and attitudes for personal and community development;
- What do you understand by ‘hidden curriculum’?
Unwritten, unofficial, and often unintended lessons, values and perspectives that students learn in schools or in the social environment.
- Give the process of curriculum development
It consists of nine stages namely:
- Need assessments: Information gathering, situational analysis and establishment of gaps
- Policy formulation: national goals, levels and subjects, number of skills areas/subjects.
- Designing of the curriculum: subject content, skills and topic objectives, scopes, and sequence charts, writing workshops, and subject panels.
- Syllabus development: writing workshops, subject panel meetings, course panel meetings, academic board meetings and printing and production of syllabuses.
- Development of curriculum support materials. Production of non-print materials, vetting of teaching and learning materials, procurement, and distribution of materials to school.
- Teacher preparation: development of training syllabuses manuals, in servicing of teachers and field officers on the new curriculum.
- Pre-testing/Piloting in sample schools- monitoring and supervision of the curriculum implementation, correction of curriculum and curriculum support materials.
- National Implementation- monitoring, supervision, and evaluation of the curriculum
- Revision, review of curriculum: syllabus revision process, subject panel, course panel and academic board.
- What is the difference between curriculum and syllabus?
Curriculum: is a broad overview of the studied courses.
Syllabus: it gives a brief overview of the course objectives, expectations, reading list, assignments etc. it’s a detailed specification of objectives and content within a defined field of study. its derived from the curriculum and shows what’s to be learned within a specified period of time.
- Give cases of interdiction where a teacher earns half salary.
Incitement, insubordination, infamous conduct, and negligence of duty.
- How many days in a year is a permanent and pensionable teacher entitled to annualleave?Maximum of thirty days.
- What are the possible verdicts of interdiction?
- From the evidence gathered the commission may;
- Revoke the interdiction
- Warn the teacher
- Suspend the teacher from duty
- Dismiss the teacher from service
- Retire the teacher in the public interest
- Dismiss and remove from the register
- Differentiate between interdiction and suspension.
Interdiction– temporary prohibition of a teacher from exercising the powers and functions of the teachers’ office pending determination of the teachers disciplinary case.
Suspension– the removal of a teacher from duty after determination of a disciplinary case.
- What are the interdiction cases where a teacher does not earn any money?
Chronic absenteeism, desertion of duty, refusal to go on transfer, having been jailed or held in legal custody, misappropriation or mismanagement of funds, forgery, fraudulent claims and receipts of funds, use of false certificates, impersonation or collusion and not of good moral conduct.
- Name the different types of leave a teacher is entitled to.
- Annualleave– max of 30 days during school holidays. apply to head of institution.
- Sickleave– max 3 months with full pay, further 3 months with half-pay
- Compassionateleave– time off duty to commiserate with immediate or expanded family in times of distress. Granted for max of 15 days in any one calendar year.
- Specialleave– granted to those traveling abroad to participate in seminars or short courses, important events etc.
- Maternityleave– granted tofemale teachers up to a max of 90 days excluding school holidays., on account of confinement,
- Studyleave– granted with or without pay to those who have taught for atleast 5 years.
- Paternityleave– granted to male teachers up to a max of 10 days during the period of spouse’s maternity leave.
- What is CBE? How is it calculated?
CBE stands for Curriculum Based Establishment. It shows the staffing requirements of an educational institution.
- Divide the total lessons for each subject by ‘27’ to get the number of required teachers per subject.
- Sum the shortfalls for principal, deputy principal and H.O. D’sand divide it with ‘27’
- Sum the results in (i) and (ii) above to get the total number of teachers required by the school.
- Get the difference between the value in (iii) and the actual number of teachers in the school to get the under/over staffing levels.
- HISTORY OF DEV’T OF EDUCATION
- Name four education commissions since independence.
Ominde report, The Wanjigi Report (GoK, 1983); The Kamunge Report (GoK, 1985), The Mungai Report (GoK, 1995); The Ndegwa Report (GoK, 1991) and The Koech Report (GoK, 1999).
- What were the recommendations of the following: (a) Ominde commission (b) Kamunge commission (c) Koech commission?
- Ominde Report 1964 — it sought to reform colonial education. It proposed one that would foster unity and create human resources for national development.
- Gachathi Report 1976 — redefined policies and emphasised national unity and socio-economic and cultural aspirations of Kenya. Proposed a nine-year primary school curriculum.
- Mackay Report 1981 — removed A-Level education and established Moi University, 8-4-4 and Commission for Higher Education.
- Kamunge Report 1988 — focused on education financing, quality, and relevance. This led to cost-sharing and abolition of students allowances in tertiary institutions & universities.
- Koech Report 1999 — proposed Totally Integrated Quality Education and Training (TIQET) and the re-introduction of pre-university opportunities in post-secondary education. The Government did not adopt it, but some proposals have been adopted.
- Odhiambo Report 2011– its focus was how re-align the education sector to vision 2030 and the constitution of Kenya 2010. It recommended a curriculum reform that gives a structure of two cycles; Basic education cycle of 14 years (2-6-3-3) which is free and compulsory and higher education cycle (2 years of middle college or 3 of university).
- Kilemi Mwiria report 2014– recommended optimal class size of 45 students, deployment of teachers and head teachers outside their home counties to foster national integration, harmonize terms of employment for support staff with that of other civil servants
- FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
- What is the deadline for submission of the Books of account for auditing?
Four months from the end of each financial year of the government.
- PROCUREMENT
- Name two members of a tender committee in a school.
- Under what circumstances can a school use direct procurement method.
- When there is only one person who can supply the goods, works or services being procured
- When there is no reasonable alternative or substitute for the goods, works or services
- There is an urgent need for the goods, works or services
- Because of the urgency, the other available methods of procurement are impractical
- The circumstance that gave rise to the urgency were not foreseeable and were not as a result of dilatory conduct on the part of the procuring entity
- What are the pitfalls in school procurement?
- CURRENT AFFAIRS
- What are the sustainable development goals?
The SDGs are a UN-sponsored effort to create a common set of development goals for all communities in every country, with a deadline for attainment of 2030.
- What is vision 2030?
It’s a national long term development blue print that seeks to create a globally competitive and prosperous nation with a high-quality life by 2030, that aims to transform Kenya into a newly industrializing middle income country providing a high-quality life to all its citizens by 2030 in a clean secure environment.
- What are the pillars of Vision 2030?
The vision is anchored on three pillars namely economic, social, and political.
Economic pillar– seeks to achieve an average economic growth rate of 10% p.a. and sustaining the same until 2030 in order to generate resources sufficient for MDGs and vision goals
Social pillar– aims to create a just, cohesive, and equitable social development in a clean and secure environment
Political pillar– seeks to realize an issue based, people-centred, result-oriented and accountable democratic system.
- What are the benefits of Devolved management in education?
- Give two functions of the County Executive in charge of Education.
- Evaluate performance of education in the county and advise the governor
- Work in partnership with county education board in establishing efficiency and effective delivery of education services in the county
- Suggest budgetary allocation for education department
- Represent the governor at county level education meetings
- Promote private investing in education.
FUNCTIONS OF THE MINISTRY OF EDUCATION
- Standards assessment and supervision of educational institutions
- Schools administration programmes
- Registration of education and training institutions
- Curriculum development
- School equipment
- ECD, care and development
- Primary and secondary education, special education, continuing education,
- Recruitment and remuneration of teachers
- Capacity building of officers and institution managers
- Publishing curricula literature
- Research authorization, co-ordination, inventory and dissemination.
VISIONOFMOE– quality education for development
MISSION– to provide, promote and co-ordinate lifelong education, training and research for sustainable development.
SCHOOL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
The school accounts are audited annually
- School financial statements
- Trail balance
- Statement of income and expenditure
- Balance sheet
- Statement of assets and liabilities
- School income sources
- Grants from MOE
- Tuition fees from MOE
- Rents
- PTA/ development levy
- Textbook fund
- Activity/sports
- Donations, parents’ contribution
- Caution
- Examination fee
- Statutory deductions e.g. NHIF, NSSF, PAYE
- Expenditure
- Recurrent expenditures
- Personal emoluments- payroll for non-teaching and support staff
- Tuition and boarding- school equipments, stores, textbooks
- Contingencies- small expenditures that cannot be accounted for in other vote heads e.g. postage, uniforms
- Local transport and travel(LT&T)
- Repairs, maintenance, and improvement (RMI)
- Examinations
- Electricity, water and conservancy (EWC)
- Activity/ Sports
- Education improvement fund (EIF)
- Non-recurrent expenditure
- Buildings
- Permanent equipment.
- Special provisions.
- Types of budgets
- Project budget- for specific project
- Period budget- all activities in the planning period
- Records used in procurement
- Local purchase order (LPO)
- Local service order (LSO)
- Records used in delivery of goods
- Delivery note
- Stores ledger
- Invoices/ job card
- Records used in receiving cash
- Receipt books
- Cash books
- Counterfoil receipt books register- recording used and un used receipt books
- Records used in paying out/ disbursing cash
- Payment vouchers
- Expenditure support documents e.g BOM minutes
- Cheque book
- Payroll
- Cash book
- Other documents
- Fees register
- Parents register
- Telephone call register
- Contracts/suppliers register
- Textbook register
- Textbook management manual
- Imprest register
- Claims register
- Stores and inventory
- Fixed assets register
- Audit file
- Cash can be withdrawn from the bank in five ways
- Cash withdrawal
- Cheque to pay suppliers
- Standing order
- Direct debit initiated by the institution e.g. bank draft
- Bank statement reconciliation
- At the end of every month, the institution compares entries in the cash book with those in the bank statement and prepare reconciliation. The purpose of reconciliation includes:
- Confirming accuracy of bank entries
- Identifying any payments or receipts in the bank but missing in the cashbooks and vice versa.
DEFINITION OF TERMS
Allowance– monetary compensation paid to a teacher in addition to the salary
Commoncadrepromotion– promotion of a teacher from one grade to the next upon completion of a specified period of service subject to meeting specified qualifications.
Deployment– appointment of a teacher to an administrative position, a higher administrative position, to the Secretariat of the commission, in an acting capacity and includes posting from primary institution to a post primary institution and withdrawal of administrative duties
Desertion– being absent from duty continuously for a period of fourteen days or more without written authority
Dismissal– decision of the commission to terminate the services of a teacher.
Embezzlement– fraudulent conversion of public funds and property entrusted to the teacher to personal use
Incitement– any act, utterance, attempt or omission on the part of a teacher directed towards learners, teachers, workers or parents in an educational institution leading to or likely to lead to breach of peace, destruction of property, bodily harm, loss of life or disruption of learning of any kind.
Insubordination– failure or refusal by a teacher to obey a lawful instruction issued by the commission or a person placed in authority by the commission
Interdiction– temporary prohibition of a teacher from exercising the powers and functions of teacher’s office pending determination of the teacher’s disciplinary case
Logbook– an official book maintained in an education institution in which a series of events taking place within the institution are recorded by date of their occurrence
Misappropriation– use of public funds for unauthorized purposes by the teacher
Mismanagement– handling of public funds or property in an inefficient, irregular or in any manner likely to cause loss to the institution
Pecuniaryembarrassment– a situation of high indebtness that a teacher would find himself after failing to live within his means occasioning financial liability that he cannot satisfy thus rendering himself unproductive.
Suspension-removal of a teacher from duty
Transfer– reassigning a teacher or head of an institution to perform teaching or administrative duties in a different institution.
Procurement– is the process of identifying, selecting and engaging suppliers of goods and services or works.
TSC
REQUIREMENTS FOR ENTRY IN THE TEACHING SERVICE
The person entering the teaching service shall:
- Obtain a valid certificate of registration
- Possess the relevant qualifications prescribed by the commission
- Possess a certificate of good conduct from the criminal investigation department
- Meet the requirements of chapter six of the constitution.
PERFORMANCE STANDARDS FOR A TEACHER
- A teacher shall comply with the following performance standards:
- Take out teaching certificate from the commission
- Undertake Professional Development Programme prescribed by the commission
- Possess the professional documents stipulated in the regulation 42 (1)(a)
- Use the appropriate teaching and learning resources where available
- Be proficient and possess mastery of the subject content
- Have mastery of appropriate pedagogical skills
- Be able to plan and effectively implement each teaching and learning activity, including theobjectives, scope, timing, and teaching resources
- Be able to assess, provide feedback and report to learners about achievement in learning
- Be professional and adhere to ethical practice
- Be prudent in the management of resources.
TEACHER’S PROFESSIONAL DOCUMENTS
- A teacher’s professional documents as stipulated in regulation 42(a)(i) of the COR are:
- A certificate registration
- Syllabi for the relevant cycle of education approved by the KICD
- Schemes of work
- Lesson plans
- Lesson notes
- Record of work
- Learners progress records
- Learners value added records
- Class attendance register
- Any other legal documents pertaining to education
ROLE OF HEAD OF INSTITUTION IN QUALITY ASSURANCE
- The head of institution shall in performing the role of quality assurance within the institution:
- Teach- undertake a reasonable teaching load
- Assignment of teaching and other official duties to teachers
- Supervise and ensure quality implementation of the curriculum
- Develop the institutional plan and ensure that institutional academic targets and objectives are met.
- Verify teachers’ professional documents
- Supervise the actual coverage of syllabus
- Ensure that teachers attend classes
- Ensure that adequate teaching and learning materials approved by KICD are available for the implementation of curriculum.
- Advice the commission on optimum curriculum based establishment in the institution
- Update the commission and other stakeholders on institutional performance
- Ensure a conducive teaching and learning environment in the institution
- Induct new teachers and ensure mentoring programmes are in place on the professional requirements as outlined in the COR.
- Offer guidance and be a role model to teachers
- Implement educational policies and co-curricular programme developed by the cabinet secretary responsible for the time being for matters of education
- Ensure maintenance of teaching standards and professional records by the teachers under his/her supervision.
- Be the custodian of the institutional records and submit returns to the commission and approved agents as required
- Produce all the relevant records and documents for inspection upon request
- Appraise all teachers under their supervision
- Offer technical advice to the Board of Management and other stakeholders in the institution to enable the institution to meet its objectives
- Implement the resolutions of the board of management in his/her capacity as its secretary
- Ensure proper management and maintenance of institutional resources.
- Perform any other role that may enhance teaching standards and professionalism among teachers.
FUNCTIONS OF TSC COUNTY DIRECTOR
- Facilitate the processing of teacher registration and enforcement of requirements for teacher registration
- Coordinate teacher recruitment at the county and ensure that the commission’s recruitment guidelines in force are adhered to
- Maintain a data base of registered teachers including the unemployed teachers within the county
- Manage aspects of teacher management as per the existing policy and guidelines within the county through recruitment, transfers, posting, receiving, and recommending teachers study leave, handling disciplinary matters as directed by secretary and identifying through a competitive process and recommending to the secretary, teachers to be deployed to administrative positions.
- Implement guidelines issued by the commission from time to time
- Maintain a data base of all administrative posts in the county
- Maintain a data bank of all teacher vacancies available at the county
- Coordinate identification and selection of candidates for Teacher Professional Development Courses within the county as per the guidelines issued by the commission from time to time
- Coordinate teacher promotion under the common cadre establishment within the county
- Ensure that teachers comply with the teaching standards prescribed by the commission
- Monitor the conduct and performance of teachers at the county level
- Oversee performance appraisal of teachers at the county level
- Submit other reports related to performance of teachers at the commission may require from time to time
- Transmit reports from heads of institution to the commission
- Supervise teachers within the county
- Advise respective county governments on matters relating to the teaching profession
- Receive and transmit teachers’ documents for processing of pension and related dues
- Perform other duty as may be assigned by the commission from time to time.
ROLE OF THE SUB COUNTY DIRECTOR
- Facilitate the processing of teacher registration
- Update and submit data on staffing levels to the county office
- Assign teachers employed by the commission to public institutions within the sub-county
- Co-ordinate teacher performance management activities within the sub-county
- Investigate allegations of professional misconduct within the sub-county
- Receive applications for transfer of service of teachers to public institutions for submission to the county office
- Receive retirement documents for processing of pension and related dues and submit to the county office
- Supervise staff within the sub-county office
- Perform any other duty as may be assigned by the county director.
ROLES OF TSC QUALITY ASSURANCE AND STANDARDS OFFICER
- Ensure educational institutions comply with performance standards
- Summon and interview teachers and any other person to provide information or material relating to standards assessment
- Request from any teacher the production of any teaching documents and materials referred to in regulation 42(1)(a).
- Carry out performance assessment and discuss the findings with the teacher concerned for purposes of corrective action and continuous improvement
- Examine and record any teaching material or document that will assist in compiling a report for purposes of preventive and corrective action
- Ensure maintenance of discipline and work ethics among teachers
- Compile reports in respect of performance standards and assessment carried out and submit the same to the commission for appropriate action
- Verify other reports from relevant agencies before the commission takes appropriate action
- Conduct joint standard assessment with other relevant government agencies
- Monitor performance of teachers in schools
- Perform all other duties as may be necessary to promote standards in teaching profession.
FUNCTIONS FOR A CURRICULUM SUPPORT OFFICER
- Identify the training needs of teachers and heads of institutions and advise the commission accordingly
- In liaison with the county director and school administrators, provide support services to teachers and to continuously advise on teaching techniques, selection of appropriate text books, lesson demonstrations and the challenges noted during assessment
- Organize and conduct, in conjunction with the county director, courses on curriculum delivery and implementation through seminars, workshops, retreats and in-service programmes
- Acquire appropriate resources including resource books, consumables, audio-visual aids and other materials necessary for teaching and learning
- Assist teachers to develop teaching aids and other reference materials
- Update teachers on curriculum changes, pedagogy, content coverage and any other emerging issues in the teaching service
- Develop work programmes for the curriculum support centres
- Visit schools, observe teaching techniques, give demonstrative lessons and advise teachers on the appropriate methods, techniques, and resources needed effective teaching and learning
- Assist teachers to develop and use appropriate teaching and learning materials
- Assist in the setting up and organization of subject panels and examination and assessment procedures in schools at the zonal level
- Provide professional guidance and counseling to teachers and disseminate information on curriculum, evaluation, text book selection and training
- Collect and submit data on school enrolment, staff establishment, staff changes and other related information
- Participate in the organization and management of co-curricular activities
- Work with quality assurance and standards officer to improve teaching and learning
- Enter an institution to perform demonstrative lessons to teachers for classroom practice
- Prepare regular progress reports for transmission to the county director
- Perform all other duties as may be necessary to promote standards in the teaching profession.
GROUNDS FOR ADMINISTRATION OF DISCIPLINARY ACTION
- Immoral behavior, including but not restricted to;
- Sexual intercourse
- Sodomy
- Lesbianism
- Sexual harassment or flirtation
- Professional misconduct including but not restricted to;
- Negligence of duty
- Lateness to duty
- Chronic absenteeism
- Desertion
- Incitement
- insubordination
- infamous conduct including but not limited to;
- drunkenness
- fighting
- conduct or behavior which in the opinion of the commission contradicts the spirit and letter of chapter six of the constitution
- forgery
- mismanagement and embezzlement of public
- any other act or conduct that is incompatible with the teaching profession.
THE ROLE OF THE SPONSOR
- Participate and make recommendations of review of curriculum, syllabus, books and other teaching aids
- Representation in the school management committees and Board of management
- Provide supervisory and advisory services in matters regarding spiritual development in schools including the appointments of chaplains at their own expense
- Maintenance of spiritual development while safeguarding the denominational or religious adherence of others
- Offer financial and infrastructural support
ROLES OF COUNTY DIRECTOR OF EDUCATION
The County Director of education shall, subject to the authority of the Cabinet secretary and in consultation with the County Government, perform the following functions;
- Implementation of educational policies
- Co-ordination and supervision of all education officers and support staff at the county level
- Management of basic education, adult continuing education, non-formal education, special needs education, tertiary and other educational programmes
- Initiating educational policies at county level
- Liaise with KNEC on management of national examinations
- Maintenance of quality assurance and standards in the county
- Management and monitoring the implementation of educational programmes
- Advising and facilitating the establishment and registration of learning institutions by the county government
- Administration of education management information system and the related information and communication technology at the county level
- Facilitating the auditing of all basic education institutions in the county
- Advise the county educational board on selection and appointment of BOM’s, school management committees, and parents associations
- Co-ordinate capacity building and development for officers, school managers, BOM and curriculum implementers
- Admissions, transfers, and discipline of students
- Co-ordination of partners and education providers in the county including links with government departments on all educational matters
- Supervision of handing and taking over in schools and educational institutions in consultation with the TSC
- Oversee the proper management and maintenance of school buildings, property, and infrastructure development
- Monitoring and evaluation of education programmes
- Management of co-curricular activities, sports education, and talent development in the basic education institutions in the county
- Any other duties assigned by the cabinet secretary.
FUNCTIONS OF EDUCATIONAL STANDARDS AND QUALITY ASSURANCE COUNCIL
- Ensure standards and maintain quality in institutions of basic education
- Administer policies and guidelines set for basic education
- Supervise and oversee curriculum implementation and delivery
- In co-operation with County Education Board, monitor the conduct of assessments and examinations in institutions of basic education
- Monitor and evaluate standards and quality in basic educations.
FUNCTIONS OF NATIONAL EDUCATION BOARD
- It collaborates with the quality assurance and standards commission and other stakeholders to promote standards in basic education and training
- Works with all relevant authorities and agencies to ensure that all the barriers to the right to quality education are removed and that the national and county governments facilitate the realization of the right to education by all Kenyans.
- Initiate guidelines for approval by the cabinet secretary on establishment of basic education institutions
- Puts measures in place to ensure all children attend and remain in school to complete basic education requirements
- Puts measures to ensure transition to the next level of education, especially for vulnerable and marginalised children is guaranteed.
FUNCTIONS OF THE COUNTY EDUCATION BOARD
The functions of the County Education Board shall be to—
(a) oversee in consultation with the county government, the operation and management of youth polytechnics, pre-primary education including early childhood care and education programmes in the county;
(b) coordinate and monitor education and training in the County on behalf of the national government and the county government;
(c) interpret national policies in education based on the county’s needs;
(d) initiate proposals for policy reforms;
(e) plan, promote, develop, and coordinate education, training and research in the county in accordance with the provisions of this Act, the national education policy and the laws and policies of the county government;
(f) collaborate with the Board of Management, the Principal, the Head Teacher, and other appropriate authorities in the management of basic schools;
(g) register and maintain a data bank of all education and training institutions within the county;
(h) monitor curriculum implementation in basic education in the county;
(i) monitor the conduct of examinations and assessments at the basic education and training levels in the county in collaboration with all the relevant national bodies;
(j) collaborate with the Teachers Service Commission on teacher management within the county;
(k) prepare and submit a comprehensive school termly annual report including Educational Management Information System data to the Cabinet Secretary on all areas of its mandate including education and training services, curriculum, policy implementation and school based audit report within the County;
(l) coordinate with all relevant agencies to ensure that all the barriers to the right to quality education are removed and with National Government to facilitate realization of the right to education within the county;
(m) put measures in place to ensure all children and youth of school going age within the county attend and stay in to complete basic education.
(n) perform such other functions as may be necessary for the better carrying out of the functions of the county education board under this Act or any other written law.
THE NATIONAL GOALS OF EDUCATION
- To foster nationalism, patriotism and promote national unity
- To promote social economic, technological, and industrial needs for national development
- To provide individual development and self fulfilment.
- To promote social equality and responsibility
- To promote sound moral and religious values
- To promote respect for and development of Kenya’s rich and varied culture
- To promote international consciousness and a positive attitude towards other nations
- To promote a positive attitude towards good health and the environment.
ROLE OF EDUCATION IN NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT
- Education is an important exit route from poverty
- It assists in the production of skilled manpower
- It increases an individual’s productivity by imparting skills and attitudes that are favourable to work
- It can reduce social and economic inequality
- It instils attitudes of cooperation, punctuality, leadership, creativity, and global citizenship
- It inculcates favourable attitudes in the whole development process by encouraging positive habits among the educated
- It promotes economic growth by raising people’s income and encouraging investment
- Evidence from parts of the world indicate that countries with high growth rates are the same ones with most educated manpower
CARDINAL PRINCIPLES FOR EDUCATION FOR ALL (EFA)
Dakar, Senegal April 2000;
- Free and compulsory primary education of good quality
- Expansion of early childhood care and to all young children
- Training and life skills for youths and adults
- Adult literacy programmes
- Eliminate gender disparities in access, progression, and completion
- Improve overall quality of education
MILLENIUM DEVELOPMENT GOALS (MDGs)
- Eradicate extreme poverty
- Achieve universal primary education
- Promote gender equality and empower women
- Reduce child mortality
- Improve maternal health
- Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases
- Ensure environmental sustainability
- Develop a global partnership for development
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS
They build on the foundation laid by the MDGs, and sought to complete the unfinished business of the MDGs and respond to new challenges. They SDGs
- End poverty in all its forms
- End hunger, achieve food security and improved nutrition and promote sustainable agriculture
- Ensure health lives and promote well-being for all at all ages
- Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all
- Achieve gender equality and empower all women and girls
- Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all
- Ensure access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all
- Promote sustained, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, full and productive employment and decent work for all
- Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive, and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation
- Reduce inequality within and among countries
- Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient, and sustainable
- Ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns
- Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts
- Conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas, and marine resources for sustainable development
- Protect, restore, and promote sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems, sustainably manage forests, combat desertification, and halt and reverse land degradation and halt biodiversity loss
- Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable, and inclusive institutions at all levels
- Strengthen the means of implementation and revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development.
THE TSC LOGO AND EXPLANATION
- The hands- symbolize TSC’s authority in teaching service. The embracing form of hands is a sign of its warmth and compassion for employees
- The motor Board- duty to review teaching standards, training, fitness to reach prospective teachers
- Map of Kenya- TSC’s area of jurisdiction.
- The black board- the teaching service
- The Book- teachers register, TSC’s policies, code Act, |Records, Knowledge, and information
- TSC letters and sun rays- supply of TSC teachers to all public schools in Kenya
- The circle and platform- the scroll with TSC motto represents the unity of purpose in its mission, flexibility and adaptability to changes
- Black- National aspiration
- Gold- Leader in teaching service
- Blue- TSC’s vision as in “the sky is the limit”
TSC |VISION
Effective service for quality teaching
MISSION
To establish and maintain a sufficient professional teaching service for educational institutions responsive to environmental changes
EDUCATION TRENDS SINCE INDEPENDENCE
Education trends refer to policy direction and changes that the education sector goes through from time to time.
The government has addressed challenges facing education using the following strategies;
- Educationalcommissions– comprise a group of people who have expertise in various fields appointed by the government to carry out a general overview. E.g. Ominde & Koech commissions.
- Educationcommittee– appointed by the government to look into specific aspects of education and make recommendation. E.g. Gachathi committee
- Presidentialworkingparty– appointed by the president to look into a particular aspect of education e.g. Mackay & Kamunge presidential working parties.
- Presidentialdegree– is an official order or directive issued by the president e.g. provision of free milk to all children in primary schools in Kenya
- Taskforce– a group formed for a short period of time to deal with a particular problem. In education, it’s usually appointed by the cabinet secretary. E.g. Odhiambo & the Kilemi Mwiria task forces.
- SessionalPapers– professional paper prepared by the responsible ministry to address inadequacies in the sector and come up with a policy framework to address these issues e.g.
- Sessional paper No. 10 of 1965 formally adopted the Ominde report and identified three urgent interventions; eradication of poverty, illiteracy, and diseases
- Sessional paper No. 6 of 1988 which adopted the Kamunge report. It laid emphasis on cost sharing in education
- Sessional paper No. 1 of 2005 which was based on the recommendations of the National conference on Education training and research of November 2003. It provides for the integration of secondary education as part of basic education cycle and established two centres of excellence in every district.
- Sessional paper No. 14 of 2012- provided the establishment of education standards and quality assurance and accreditation commission (ESQAC), National education board (NEB), county education board (CEB) and reforming curricular to align it with the provisions of the 2010 Constitution and the aspirations of Kenya vision 2030.
CHAPTER SIX OF CONSTITUTION OF KENYA, 2010
Cap 73 (2) Guiding principles of leadership and integrity
- Selection on the basis of personal integrity, competence and suitability, or election in a free and fair election
- Objectivity and impartiality in decision making, and in ensuring that decisions are not influenced by nepotism,favouritism, and other improper motives or corrupt practices.
- Selfless service based solely on the public interest, demonstrated by honesty in the execution of public duties and the declarationof any interest that may conflict with public duties
- Accountability to the public for decisions and actions
- Discipline and commitment in the service to the people.
CHAPTER FOUROF CONSTITUTION OF KENYA, 2010
Cap 53 (1) CHILDREN’S RIGHT
Every child has a right to:
- To a name and nationality from birth
- To free and compulsory basic education
- To basic nutrition, shelter, and health care
- To be protected from abuse, neglect, harmful cultural practices and punishment, and hazardous and exploitative labour
- To parental care and protection, which includes equal responsibility of the mother and father to provide for the child, whether they are married to each other or not
- Not to be detained, except as a measure of last resort, and when detained, to be held-
- For the shortest appropriate period of time
- Separate from adults and in conditions that take account of the child’s sex and age.

 TSC Circular on Updating of data on registered teachers not currently employed by the Teachers Service Commission
TSC Circular on Updating of data on registered teachers not currently employed by the Teachers Service Commission Mwalimu National Sacco Loans & Repayment Schedule (BOSA Loans)
Mwalimu National Sacco Loans & Repayment Schedule (BOSA Loans)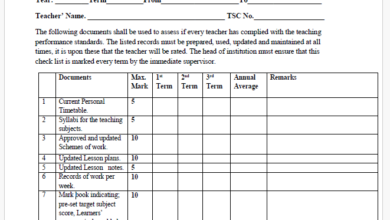 Latest TPAD Teacher’s Checklist of TSC Professional Documents
Latest TPAD Teacher’s Checklist of TSC Professional Documents Official Kuppet BBF Guidelines For All Branches
Official Kuppet BBF Guidelines For All Branches